Guest Post: Solar Electric Power in the USA
Recently, I read a report about solar power in USA. I feel it’s very interesting. So I select a part of the reports for our readers.
Solar Electric power also called photovoltaic, is the term used to describe the conversion of sunlight directly to electricity. The solar cells available today use semiconductor materials. To create useful amount of power, they are wired together in varying numbers to create solar modules (or solar panels). Because the electric grid provides AC power, the systems also include inverters that convert the DC electricity to AC electricity. Then the solar powered could be used for solar lighting, water heater and many other applications. Currently, over 2000 MW of modules are being manufactured annually worldwide.
Solar electric energy has been one of the fastest growing markets in the world for nearly two decades. A key to element of this expansion has been a steady decline in costs for technology driven by improved efficiency, improved manufacturing and economies of scale. These trends are strengthened by increasing global consciousness of climate changes and dwindling conventional resources.
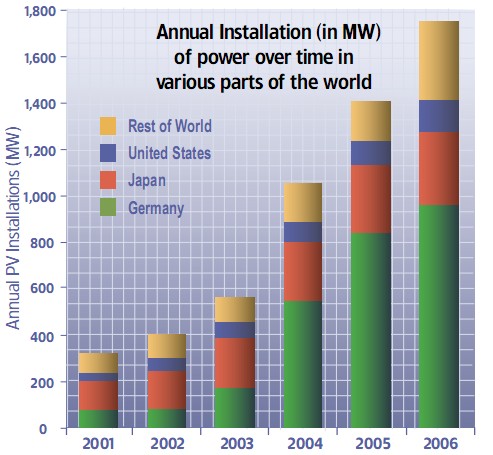
As a result, the global market is booming. In 2006, annual installation of systems around the world exceeded 1700MW. In fact, more than half of all systems worldwide were installed the last three years. The US market grew at a robust 33% in 2006. Germany’s commitment to expand the industry has enabled nearly 1,000MW to be installed in 2006 accounting for 55% of the world market. Japan led the world until recently and still comprises 17% of the word market. Also the most common application for solar power is solar street lights and solar water heater.
It is obvious that the US solar market didn’t grow much in the past several years. The Germany has only 4 times the population of New York but now has 300 times more installed capacity. The US offers substantial growth opportunity relative to Germany.
The US Solar Department of Energy developed a national solar power industry roadmap in 2004 which established a goal “To provide half of all new US electricity generation by 2015”.
As part of Governor’s Million Solar Roofs Program, California established the goal in 2006 of creating 3,000 MW of new solar electricity by 2017. A 10-year, $3 billion “Go Solar California Initiative” is underway paid for by a surcharge on ratepayer’s electric bills, estimated to cost a residential electric customer about $16 per year.
In April 2006, the New Jersey Board of Public Utilities approved an Expanded Renewable Portfolio Standard which calls for 20% Class I Renewables by 2020 and includes a minimum requirement of 2% New Jersey Solar, corresponding to 1,500 MW.
Pennsylvania has approved a solar standard within the existing Alternative Energy Portfolio Standard that would bring the state to approximately 800 MW by 2021.
About 3 quarters of the solar power of the US is installed in the California. That’s also the reason why we establish Greenshine in California.



