From Guest Blogger Dan McKee: Role of HVAC Systems in Sustainable Development
Heating, ventilating and air-conditioning (HVAC) plays a crucial role in today’s times, not just to help keep our homes and offices comfortable, but also in the development of sustainable and environmentally sound infrastructure. As we move towards sustainable cities and “green buildings”, newer HVAC mechanisms and technologies are the way forward, offering as they do the dual benefits of high performance and adaptability.So, what are “green buildings”? A typical green building would be energy and resource efficient, non-polluting and waste efficient, flexible and easily scalable, as well as easy to operate. These buildings would utilize a “life cycle approach” to water and energy usage, and would be continually evolving in efficiency and adaptability.
HVAC and Sustainability Issues
Historically, the maintenance and operation of HVAC systems has focused on complying with statutory requirements for health and safety and providing occupant comfort, with little consideration given to long term value for money. Therefore, opportunities for achieving energy and efficiency gains have been missed and lifecycle costs not given due diligence.
Energy conservation, indoor air quality, and comfort are among the core green building issues, typically brought on by heating, air-conditioning and ventilation design. Many of these interrelated systems can be complex, expensive to install, and costly to operate, but green building also offers many opportunities to simplify and save, especially with the use of correctly-managed HVAC systems.
Benefits of Well-Managed HVAC Systems
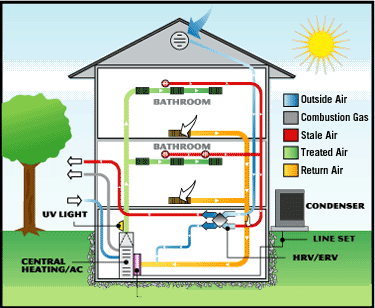
An HVAC system is more than just a few pieces of mechanical equipment – it’s a system designed as part of the house. In a green home, heating and cooling equipment can be smaller, less costly, and less complicated than similar systems in large commercial establishments or buildings.
- Insulation and thermal cover of the buildings plays a pivotal role in protecting the building from energy loss and waste. Well-designed ventilation systems also play a crucial role in making the HVACs better for use.
- An HVAC system works best when it also takes local climate and building designs into account. High-performance glazing and sun control can help reduce the load and thereby the size required of the HVACs, making them more sustainable and affordable.
- Central to this premise of thinking small are the many passive solar features built into a green house. HVAC design follows other fundamental building steps that can collectively reduce the size of the heating and cooling system by 30-50%.
- Solar orientation, insulation, window locations and design, even vegetation on the building site all directly affect heating and cooling loads. Designing a system based on real demand, not conventional practice, is essential.
Best Practice in Sustainable HVAC
Traditional HVAC systems can, if not used properly, damage the environment through the use of energy and fossil fuels, thereby polluting the surrounding atmosphere and depleting resources. The best solution is to use and build HVAC systems that use less energy, and some key HVAC installation best practices include:
- Incorporate HVAC systems early in the design phase
- Size HVAC system to meet actual loads
- Specify high-efficiency furnaces and air conditioning units
- Seal around electrical outlets and all wall penetrations
- Insulate all ducts in the attic or crawl space
- Design adequate returns to keep the house pressure balanced
- Install a heat recovery ventilation system
Keeping these in mind, one can rarely go wrong while installing a good HVAC for their office or residential projects. Not only will the investment bear returns in the form of economical and affordable air conditioning systems, but also comfortable indoor spaces!